In the realm of virtual reality, the concept of Degrees of Freedom (DoF) plays a pivotal role in determining how users interact with and navigate within immersive VR spaces. DoF refers to the number of axes on which a user’s movements are tracked, directly influencing the realism and immersion of a VR experience by accounting for head and space movements. As technology advances, the distinctions between 3DoF and 6DoF VR headsets, like the Oculus Quest 2, become crucial for developers and users alike, setting a new standard for immersive VR by enhancing how participants move and engage within a virtual environment.
Comparing 3DoF with 6DoF unveils significant differences in virtual reality applications, from simple VR training programs to complex, immersive VR gaming. While 3DoF limits movement to rotational axes, 6DoF introduces positional tracking, allowing for a more natural and engaging interaction within the VR space. This transition not only marks a technological evolution in VR headsets but also elevates user experiences, paving the way for broader adoption and innovative applications of virtual reality.
Understanding Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
Degrees of freedom (DoF) in virtual reality (VR) dictate how users can interact with and move within a virtual environment. This section explores the fundamental differences and functionalities of 3DoF and 6DoF, which are crucial for understanding VR technology.
3 Degrees of Freedom (3DoF)
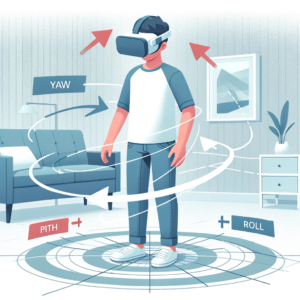
- Rotational Movements Only: 3DoF allows users to rotate their head in three planes: pitch, yaw, and roll, enabling basic head movements like looking left, right, up, or down.
- Applications: Suitable for static VR experiences such as watching 360-degree videos or simple VR training scenarios where extensive movement is not required.
6 Degrees of Freedom (6DoF)
- Rotational and Translational Movements: In addition to the rotational movements provided by 3DoF, 6DoF includes translational movements along three axes: sway (left/right), heave (up/down), and surge (forward/backward), allowing users to move freely in 3D space.
- Enhanced Realism and Interaction: This capability not only enhances the realism of the VR experience but also allows for complex interactions and movements, such as dodging obstacles or moving towards objects within the VR environment.
Impact on User Experience
- Increased Engagement and Realism: A higher number of DoF significantly enhances user engagement by allowing more natural and complex movements.
- Reduction of Visual Fatigue: Incorporating more DoF can improve depth perception, stabilize image fixation, and reduce visual fatigue, making the VR experience more comfortable.
- Minimized Discomfort: By accurately tracking both head and body movements, 6DoF systems reduce the discrepancies between visual and sensory inputs, which helps in minimizing motion sickness and discomfort.
Technological Implementation
- Tracking Technologies: 6DoF utilizes advanced tracking technologies such as inside-out tracking, which is integral to modern VR headsets for precise movement detection.
- VR Headset Varieties: VR and mixed reality headsets are typically designed to offer either 3-DoF or 6DoF, depending on their intended use and complexity of the VR applications they support.
This detailed understanding of DoF not only highlights the technological evolution within VR systems but also assists users and developers in selecting the right type of headset based on their specific needs and the level of interaction required.
Technological Evolution from 3DoF to 6DoF
The evolution from 3DoF to 6DoF in virtual reality (VR) marks a significant technological leap, enhancing how users interact within virtual environments. Initially, VR systems like the Oculus Rift, developed by Palmer Luckey in 2011, relied on basic 3DoF tracking, which limited movement to rotational axes only. This early technology used components from readily available hardware, such as screens from Samsung Galaxy Note devices, to create immersive experiences.
As the industry advanced, the introduction of 6DoF allowed for a more dynamic interaction by tracking both the position and orientation of the head in space. This shift was facilitated by the integration of sophisticated sensors and cameras within the VR headsets, enabling not just rotational but also translational movements—forward/backward, up/down, and left/right. These advancements significantly increased the immersion and realism of VR environments, making them more engaging and versatile.
The expansion of VR’s capabilities also brought about a diversification in the hardware used to enhance these experiences. Modern VR systems now employ a variety of input devices such as motion trackers, treadmills, and sensing gloves, which work in tandem with the headsets to provide a fully immersive experience. Additionally, the software landscape has grown to support these advancements, with tools ranging from game engines to content management systems specifically designed for VR.
Significant too is the shift towards untethered 6DoF headsets, which offer users freedom from the constraints of external cameras and cables. Modern systems use inside-out tracking, where cameras on the headset itself scan the environment, allowing for precise movement tracking without the need for external hardware. This development not only enhances user convenience but also broadens the potential applications of VR technology in various fields.
The progression to 6DoF has also been supported by improvements in computational power and sensor technology. Advances in “inside-out” tracking systems have reduced the complexity and cost of VR setups, making 6DoF experiences more accessible to a wider audience. These technological enhancements are expected to continue driving the VR market, which is projected to reach a valuation of nearly 300 billion USD by 2024.
Overall, the transition from 3DoF to 6DoF in VR represents a fundamental shift in how virtual environments are experienced, offering users a much more interactive and immersive way to explore digital worlds.
Comparing 3DOF and 6DOF in VR Applications
Tracking Capabilities and Content Suitability
- Degrees of Freedom Explained:
- 3DoF devices track rotational movements only—rolling, yawing, and pitching—suitable for viewing 360-degree videos where spatial movement is not required.
- 6DoF devices add translational movements—sway, surge, and heave—enabling users to move freely in a simulated 3D environment, crucial for interactive applications like immersive VR training.
- Application Specifics:
- For passive experiences such as watching films or 360 videos, 3DoF headsets are recommended due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- 6DoF headsets are preferable for dynamic and interactive environments where users can walk around and interact with the virtual space, making them ideal for immersive training and educational purposes.
Technological and User Experience Implications
- User Interaction and Immersion:
- 6DoF allows for a more engaging and realistic experience as it tracks both head and body movements, enhancing the feeling of presence in virtual environments.
- 3DoF, while limited to head rotations, is effective for short, seated experiences or scenarios where detailed interaction with the environment is unnecessary.
- Comfort and Accessibility:
- 6DoF systems, by tracking full body movements, minimize the risk of motion sickness and visual discomfort by aligning virtual and physical movements more closely.
- 3DoF systems, being less complex, are more accessible and cost-effective, suitable for entry-level VR experiences and educational tools that do not require extensive user movement.
Market Trends and Investment Insights
- Economic Considerations:
- The trend towards 6DoF reflects its growing importance in providing comprehensive and immersive VR experiences, which, while more expensive, offer greater long-term value and user satisfaction.
- Investing in 6DoF technology is seen as more future-proof, whereas 3DoF is becoming less popular due to its limitations in interactive VR applications.
- Content Compatibility:
- 6DoF headsets are versatile, capable of handling both 3DoF and 6DoF content, providing users with a wide range of VR experiences.
- 3DoF headsets, on the other hand, are restricted to content that requires only rotational movement, limiting their usability as the VR market evolves.
Conclusion
Through this comprehensive analysis, we have delved into the fundamental differences between 3DoF and 6DoF technologies in virtual reality, uncovering the pivotal role they play in shaping the user experience. By transitioning from simple rotational tracking to encompassing full spatial movements, 6DoF offers a degree of realism and immersion that sets a new benchmark for virtual environments. This evolution not only enhances user engagement by allowing for more natural interactions but also reduces discomfort, marking a significant leap in the technological capabilities of VR systems.
As we look towards the future of virtual reality, the shift from 3DoF to 6DoF signifies a wider trend towards creating more inclusive, realistic, and versatile digital experiences. While 6DoF emerges as the superior technology for interactive and immersive applications, understanding the appropriate application of each technology based on user needs and content requirements remains key. The ongoing advancements in VR technology underscore the importance of selecting the right degree of freedom for the right application, spotlighting the endless possibilities for innovation and application in the realm of virtual reality.
FAQs
What distinguishes 3DoF from 6DoF?
3DoF (Three Degrees of Freedom) tracks only rotational movements, meaning it can detect when a user turns their head left or right, tilts it up or down, or pivots it left or right. In contrast, 6DoF (Six Degrees of Freedom) tracks both rotational and translational movements, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the user’s head position and orientation in 3D space.
What is the significance of 6DoF in virtual reality?
In virtual reality, 6DoF stands for Six Degrees of Freedom and is crucial for creating a realistic and immersive VR experience. It accounts for the user’s head position, movement, and orientation by considering both translation (movement through space) and rotation (orientation in space).
How does 3DoF function in VR?
3DoF technology in VR headsets is designed to track the rotational motion of a user’s head. This means that the system can detect when a user looks left or right, or rotates their head up or down, but it does not track forward, backward, or side-to-side movement.
Can you explain what 3DoF entails?
3DoF, or Three Degrees of Freedom, is a term used in virtual reality to describe the range of movement that a user can experience. With 3DoF, users are able to look left and right, look up and down, and pivot left and right. However, this does not include moving forward, backward, or side-to-side.